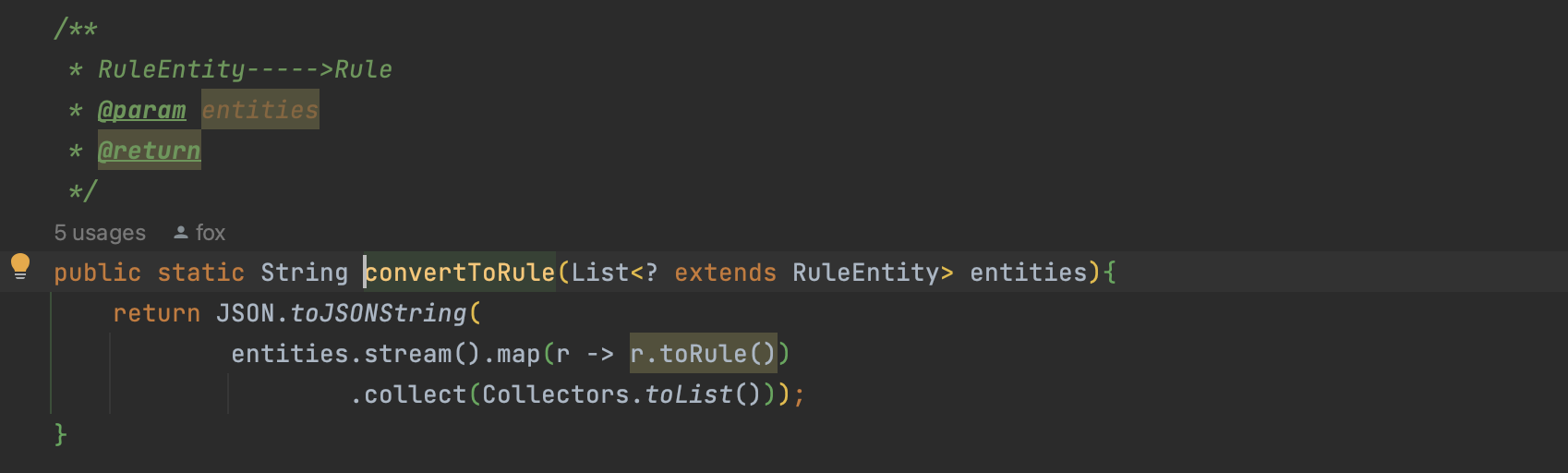
当sentinel dashboard配置规则后推送给微服务,微服务会存在内存中,但是一旦重启 规则就会消失,这种方式并不建议在生产环境中使用,为此我们需要对sentinel的源码进行改造,让他支持持久化。
Sentinel持久化模式 Sentinel一共有3种推送模式:
推送模式
说明
优点
缺点
原始模式
API 将规则推送至客户端并直接更新到内存中,扩展写数据源(WritableDataSource)
简单,无任何依赖
不保证一致性;规则保存在内存中,重启即消失。严重不建议用于生产环境
Pull 模式
扩展写数据源(WritableDataSource), 客户端主动向某个规则管理中心定期轮询拉取规则,这个规则中心可以是 RDBMS、文件 等
简单,无任何依赖;规则持久化
不保证一致性;实时性不保证,拉取过于频繁也可能会有性能问题。
Push 模式
扩展读数据源(ReadableDataSource),规则中心统一推送,客户端通过注册监听器的方式时刻监听变化,比如使用 Nacos、Zookeeper 等配置中心。这种方式有更好的实时性和一致性保证。生产环境下一般采用 push 模式的数据源。
规则持久化;一致性;快速
引入第三方依赖
一句话总结:生产环境建议使用Push 推送模式,而客户端通过监听器来监听配置中心的配置的变化而更新sentinel规则。
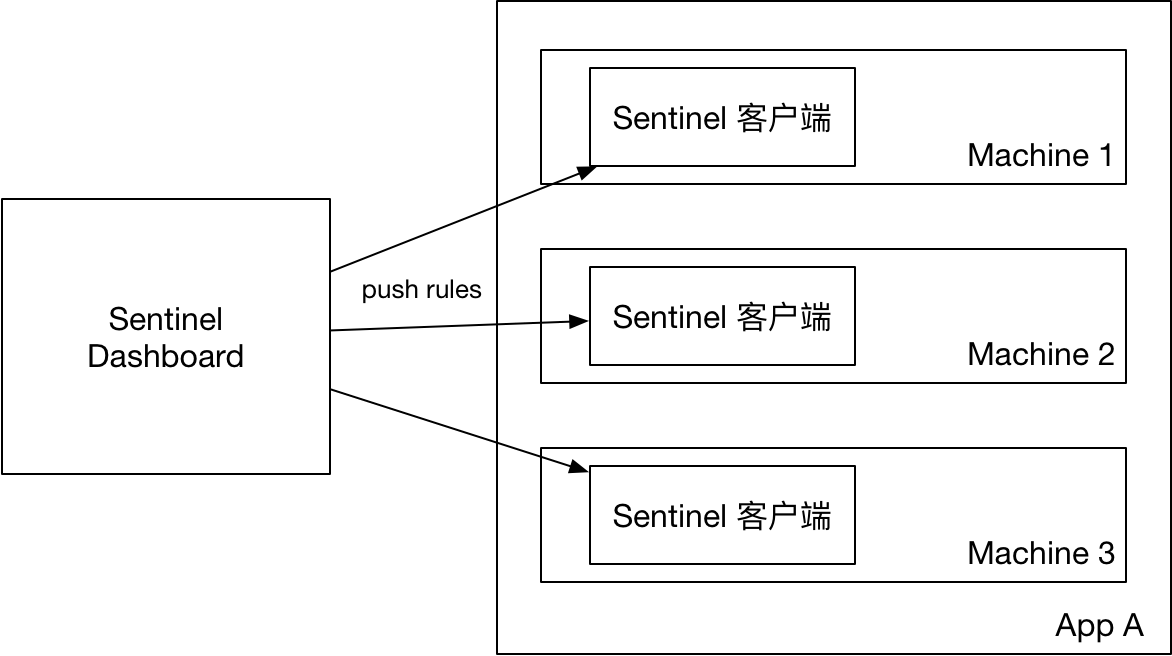
1)原始模式 Dashboard 的推送规则方式是通过 API 将规则推送至客户端,而客户端会更新到内存中:
缺点:由于规则是保存在内存中并没有进行持久化,当客户端重启后,规则就会丢失,该模式强烈不建议在生产环境中使用。
2)pull 拉模式
首先 Sentinel 控制台通过 API 将规则推送至客户端并更新到内存中,接着注册的写数据源会将新的规则保存到本地的文件中。使用 pull 模式的数据源时一般不需要对 Sentinel 控制台进行改造。这种实现方法好处是简单,坏处是无法保证监控数据的一致性。
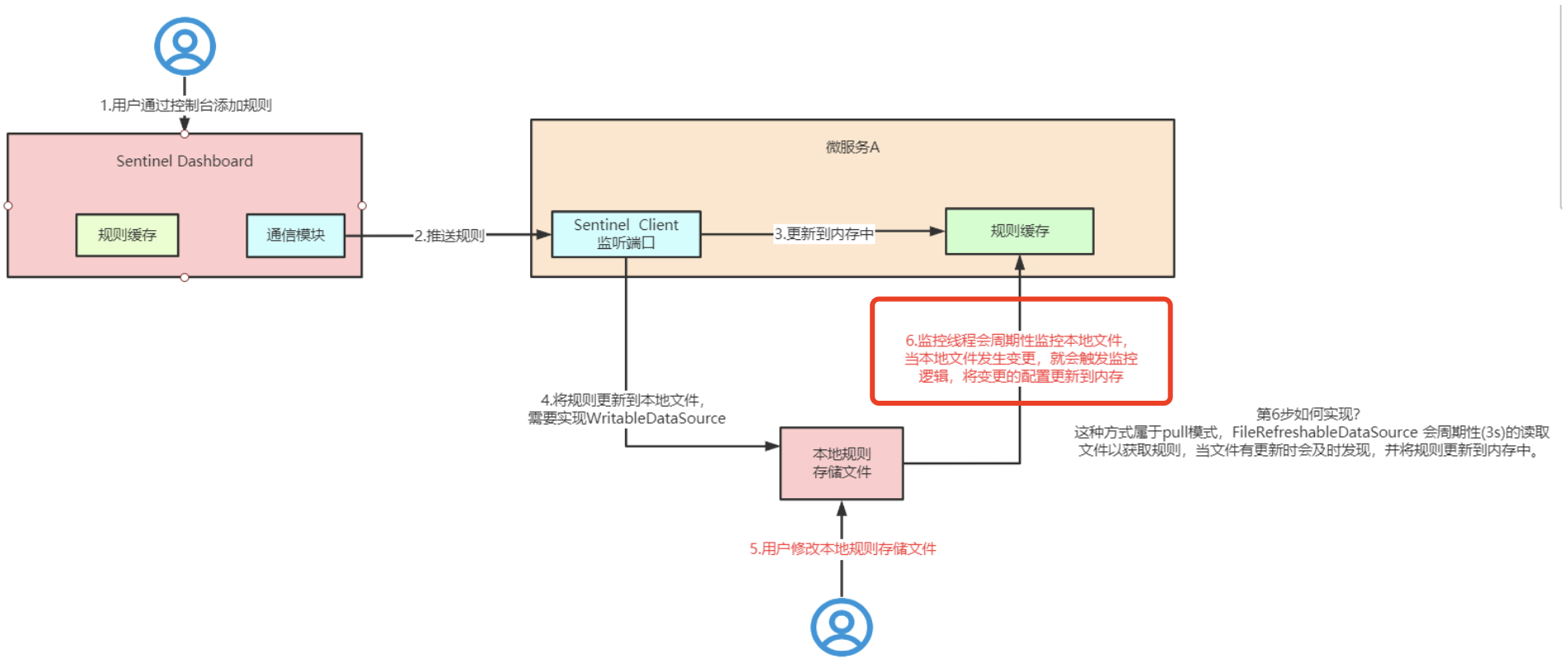
持久化流程
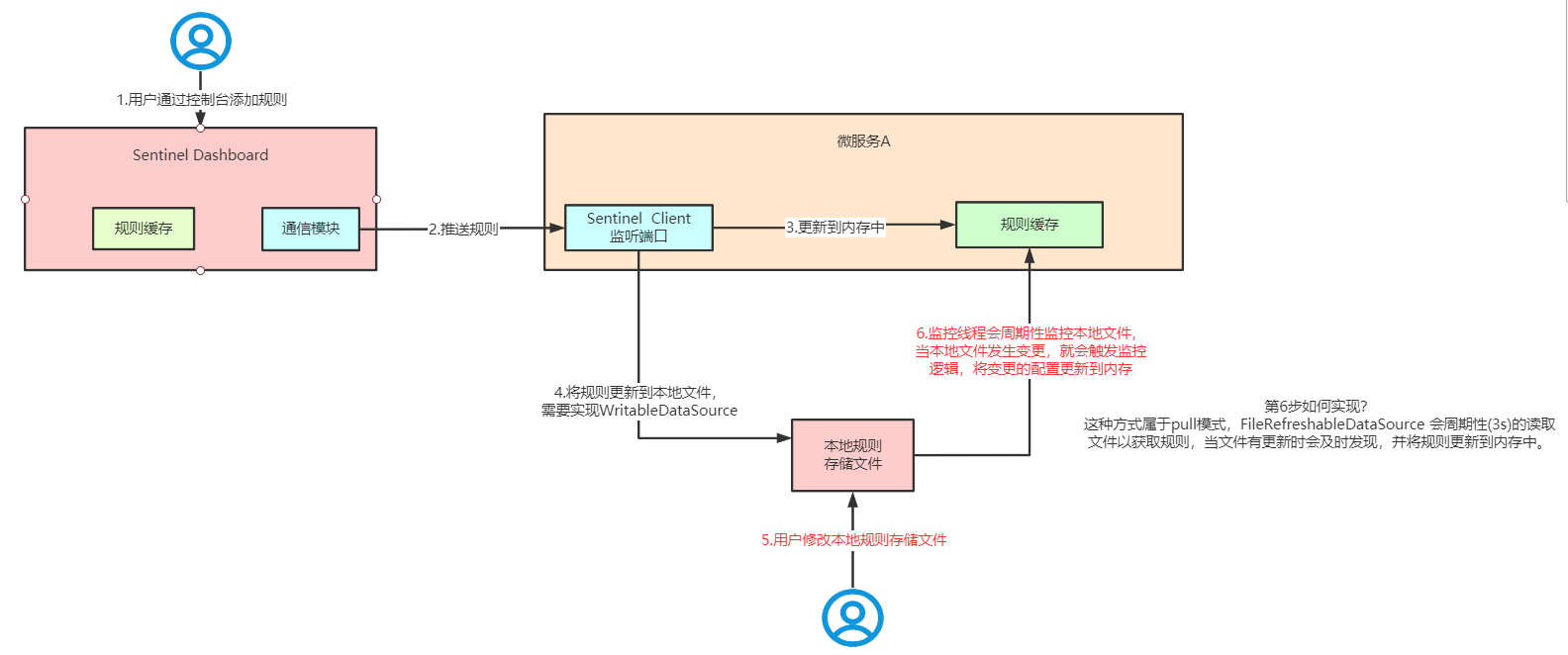
用户通过控制台添加规则
sentinel dashboard通过通信模块,推送给微服务模块的sentinel client
sentinel client更新到内存中并且 通过实现WritableDataSource接口,把规则保存到本地文件中
微服务A会有一个监控现场去监听本地文件的变化,当本地文件MD5发生变化后,就会把 最新的本地文件覆盖到内存中
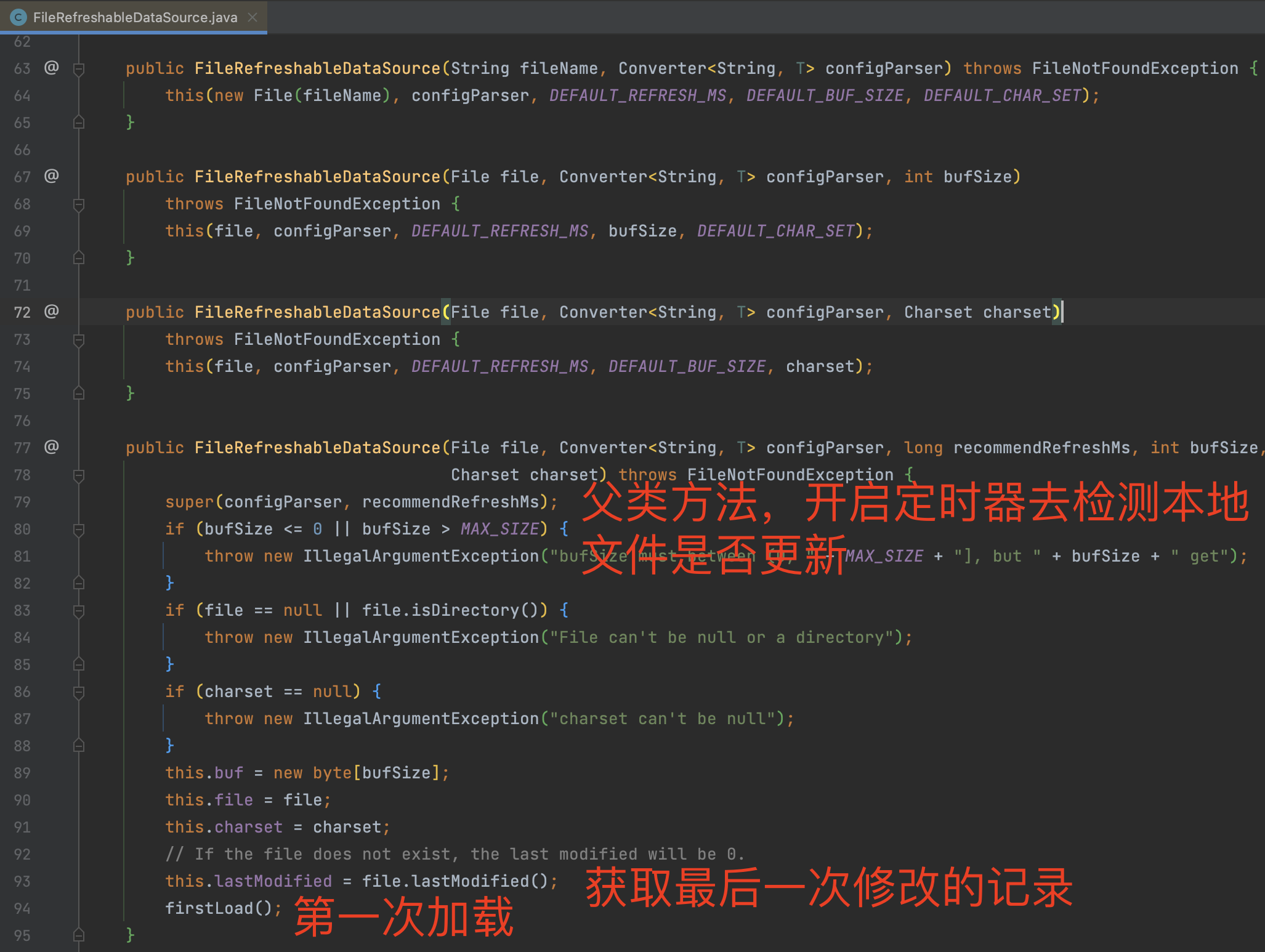
2.1 pull模式核心源码 FileRefreshableDataSource
会周期性(默认3秒)的去获取策略文件并解析规则,如果发现文件发现了变动,就会将规则更新到内存中
父类方法会创建一个定时任务,每3秒去检测一次 本地文件是否更新,如果更新的话就加载最新的配置文件到内存中。
读取配置方法
2.2 改造的扩展点 在改造pull模式之前,我们可以根据不同的框架来决定采用哪个扩展点进行 改造,不同的框架扩展点不同,具体如下:
spi
这里我们通过sentinel自己的spi接口来实现持久化
spring
beanPostProcessor
beanFactoryPostProcessor
SmartInitializingSingleton
ApplicationListener
FactoryBean
springBoot
2.3 改造pull模式 引入pom依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > com.javaxing</groupId > <artifactId > sentinel-datasource-extension-pull</artifactId > <version > 1.0.0</version > </dependency > </dependencies >
引入私人仓库
上面的依赖,主要是实现了对pull的持久化改造,我们给他打包jar包上传到了私人的maven仓库,所以要在项目中引入该仓库
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <repositories > <repository > <id > nexus-xu</id > <name > Nexus Central</name > <url > https://maven.javaxing.com/repository/sentinel/</url > <layout > default</layout > <releases > <enabled > true</enabled > </releases > <snapshots > <enabled > true</enabled > </snapshots > </repository > </repositories >
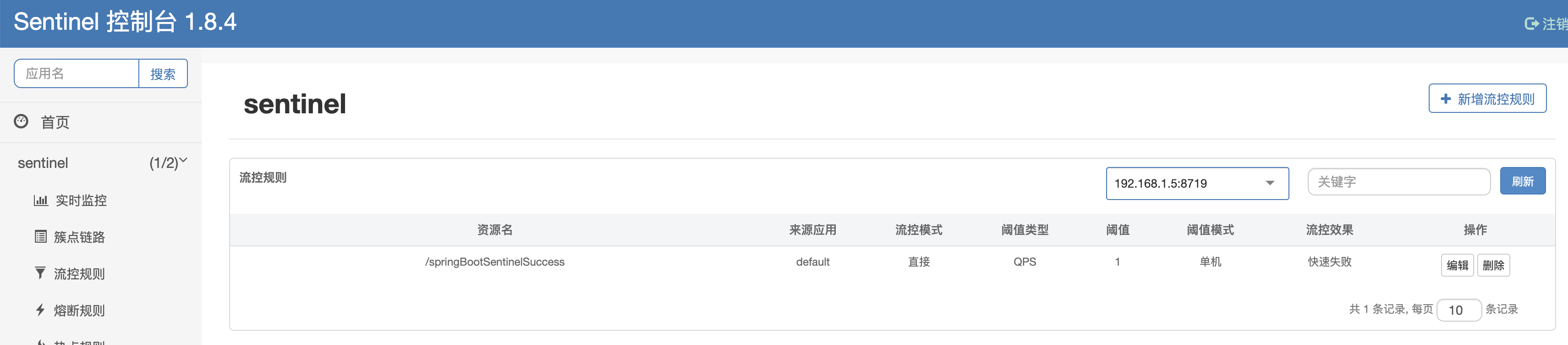
测试改造效果
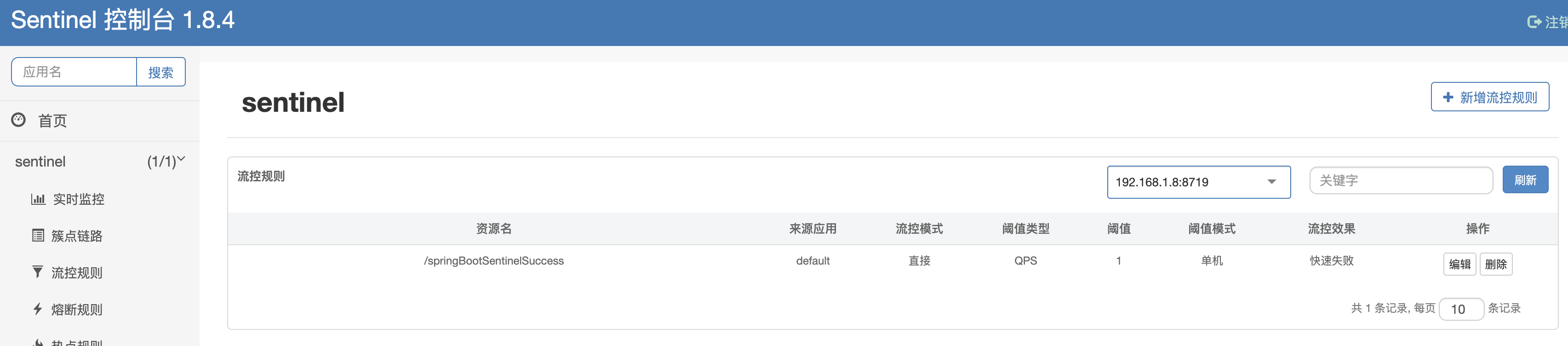
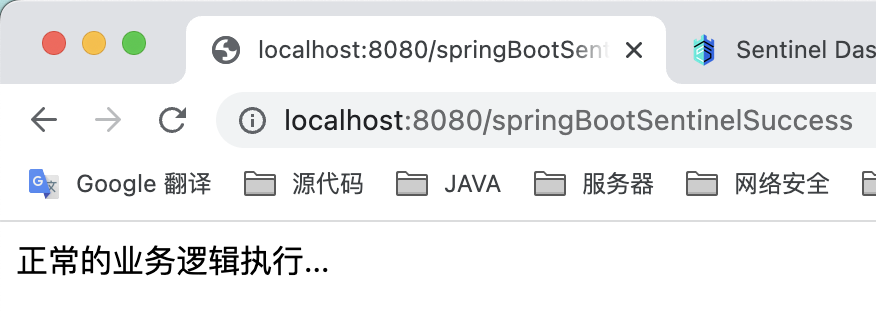
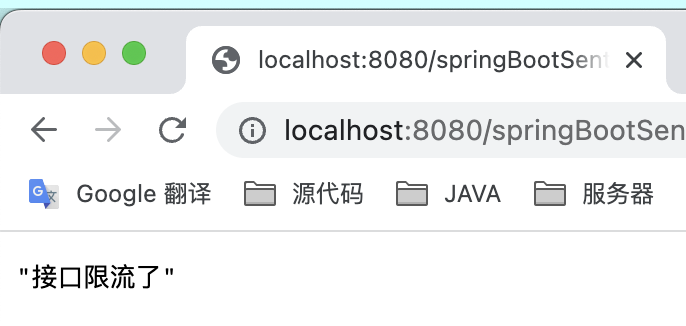
我们通过sentinel设置策略,QPS 阈值为1 ,1秒内访问2次就会被限流:
重启服务端
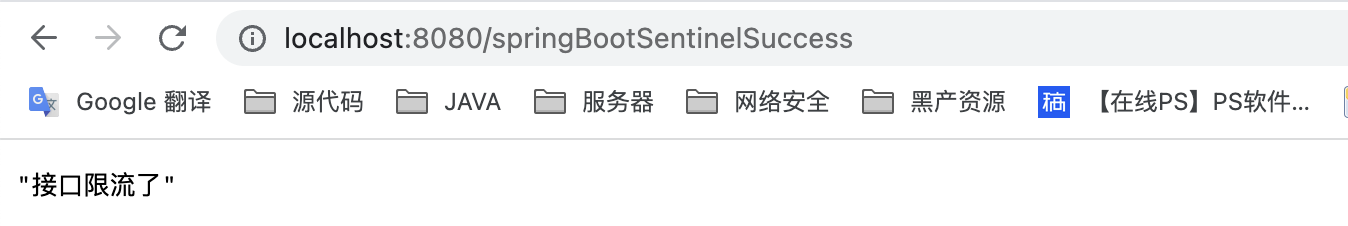
一般情况下,当我们 java服务端重启后,再次访问该controller后,sentinel dashboard的流控规则会丢失。但是由于我们引入了pull改造依赖包,当重启后,流控规则不会消失。
再次访问controller:
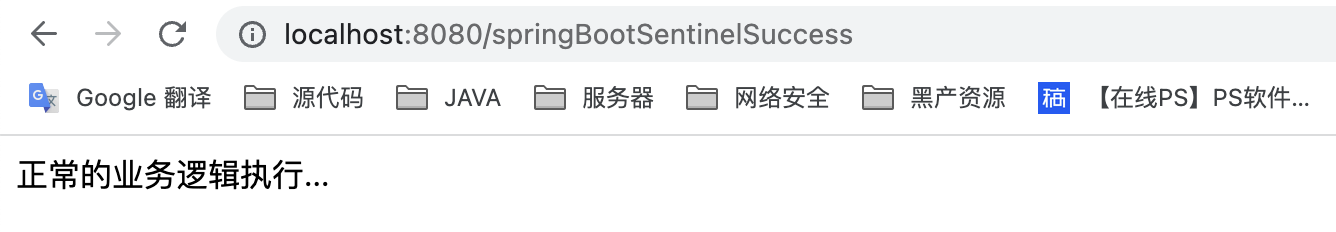
sentinel dashboard控制台
控制台的流控规则依然存在,因为当服务重启后会从本地文件中拉取规则到内存中,并创建一个定时任务去监听该本地文件,如果该文件发生了变动的话会马上更新到内存中。如果控制台会从服务中的内存拉取规则到控制台。
2.4 pull拉模式改造细节 2.3 我们引入了jar包后,直接可以实现pull模式的持久化,但是具体是如何实现的呢,下面我们来大致的分析一下实现的代码。
实现InitFunc接口,在init中处理DataSource初始化逻辑,并利用spi机制实现加载。
核心实现代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 package com.javaxing.sentinel.extension.filepull;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.command.handler.ModifyParamFlowRulesCommandHandler;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.FileRefreshableDataSource;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.FileWritableDataSource;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.ReadableDataSource;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.WritableDataSource;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthorityRule;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthorityRuleManager;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRule;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRuleManager;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRule;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRuleManager;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.param.ParamFlowRule;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.param.ParamFlowRuleManager;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRule;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRuleManager;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.transport.util.WritableDataSourceRegistry;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.util.List;public class FileDataSourceInit implements InitFunc { @Override public void init () throws Exception { RuleFileUtils.mkdirIfNotExits(PersistenceRuleConstant.storePath); RuleFileUtils.createFileIfNotExits(PersistenceRuleConstant.rulesMap); dealFlowRules(); dealDegradeRules(); dealSystemRules(); dealParamFlowRules(); dealAuthRules(); } private void dealFlowRules () throws FileNotFoundException { String ruleFilePath = PersistenceRuleConstant.rulesMap.get(PersistenceRuleConstant.FLOW_RULE_PATH).toString(); ReadableDataSource<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource ( ruleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.flowRuleListParser ); FlowRuleManager.register2Property(flowRuleRDS.getProperty()); WritableDataSource<List<FlowRule>> flowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource <List<FlowRule>>( ruleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.flowFuleEnCoding ); WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerFlowDataSource(flowRuleWDS); } private void dealDegradeRules () throws FileNotFoundException { String degradeRuleFilePath = PersistenceRuleConstant.rulesMap.get(PersistenceRuleConstant.DEGRAGE_RULE_PATH).toString(); ReadableDataSource<String, List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource ( degradeRuleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.degradeRuleListParse ); DegradeRuleManager.register2Property(degradeRuleRDS.getProperty()); WritableDataSource<List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource <>( degradeRuleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.degradeRuleEnCoding ); WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerDegradeDataSource(degradeRuleWDS); } private void dealSystemRules () throws FileNotFoundException { String systemRuleFilePath = PersistenceRuleConstant.rulesMap.get(PersistenceRuleConstant.SYSTEM_RULE_PATH).toString(); ReadableDataSource<String, List<SystemRule>> systemRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource ( systemRuleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.sysRuleListParse ); SystemRuleManager.register2Property(systemRuleRDS.getProperty()); WritableDataSource<List<SystemRule>> systemRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource <>( systemRuleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.sysRuleEnCoding ); WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerSystemDataSource(systemRuleWDS); } private void dealParamFlowRules () throws FileNotFoundException { String paramFlowRuleFilePath = PersistenceRuleConstant.rulesMap.get(PersistenceRuleConstant.HOT_PARAM_RULE).toString(); ReadableDataSource<String, List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource ( paramFlowRuleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.paramFlowRuleListParse ); ParamFlowRuleManager.register2Property(paramFlowRuleRDS.getProperty()); WritableDataSource<List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource <>( paramFlowRuleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.paramRuleEnCoding ); ModifyParamFlowRulesCommandHandler.setWritableDataSource(paramFlowRuleWDS); } private void dealAuthRules () throws FileNotFoundException { String authFilePath = PersistenceRuleConstant.rulesMap.get(PersistenceRuleConstant.AUTH_RULE_PATH).toString(); ReadableDataSource<String, List<AuthorityRule>> authRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource ( authFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.authorityRuleParse ); AuthorityRuleManager.register2Property(authRuleRDS.getProperty()); WritableDataSource<List<AuthorityRule>> authRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource <>( authFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.authorityEncoding ); WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerAuthorityDataSource(authRuleWDS); } }
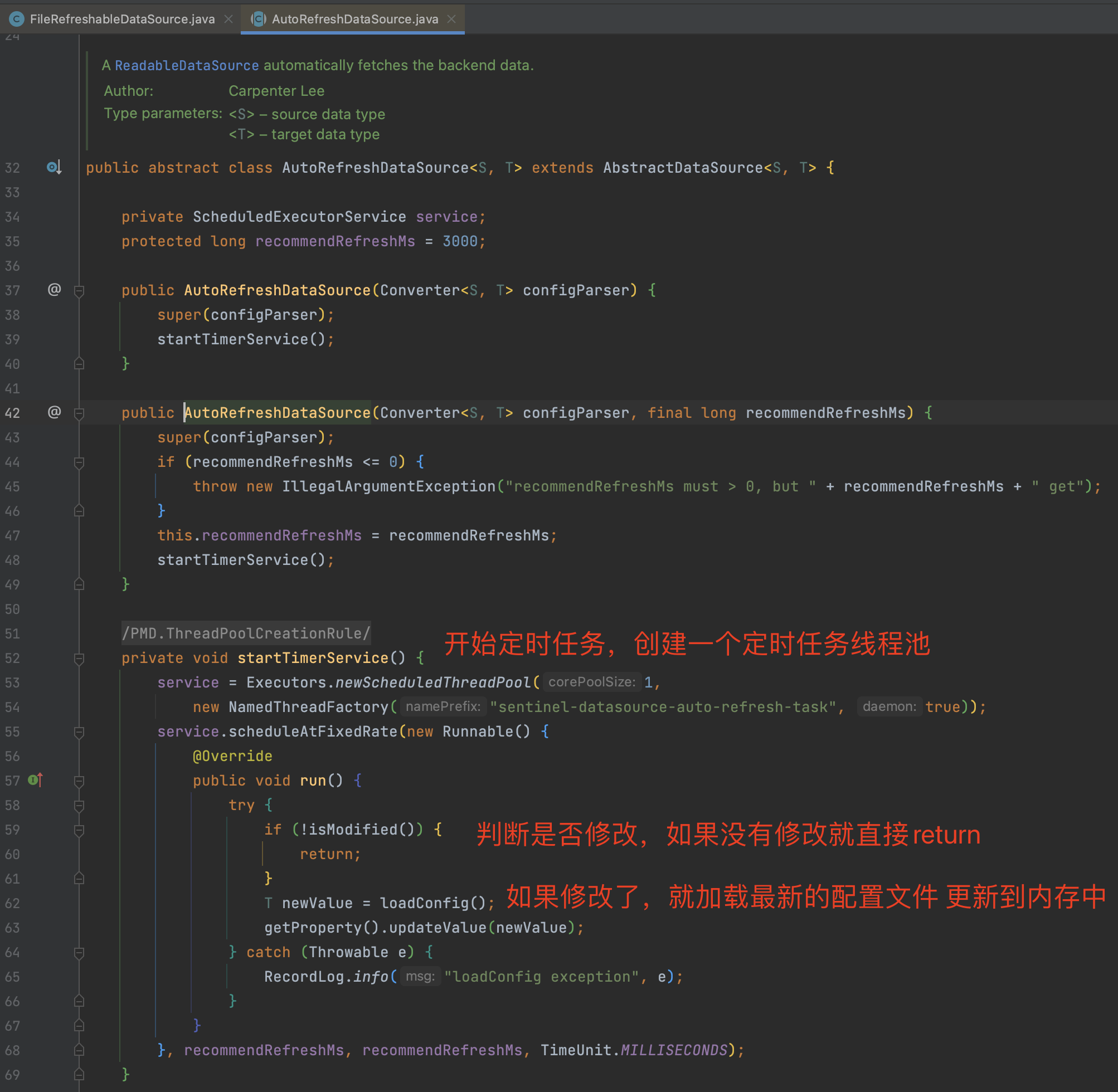
3)push 推模式 3.1 pull模式的缺点 1、限流策略的实时性
由于我们pull模式会在本地创建一个线程,该线程会创建一个定时任务 每3秒去检测一下本地策略文件是否发生变更,变更的话就把文件更新到内存中。
定时任务是每3秒检测一次,如果我们推送了策略后,就会存在2秒的真空期,无法做到策略的实时性。
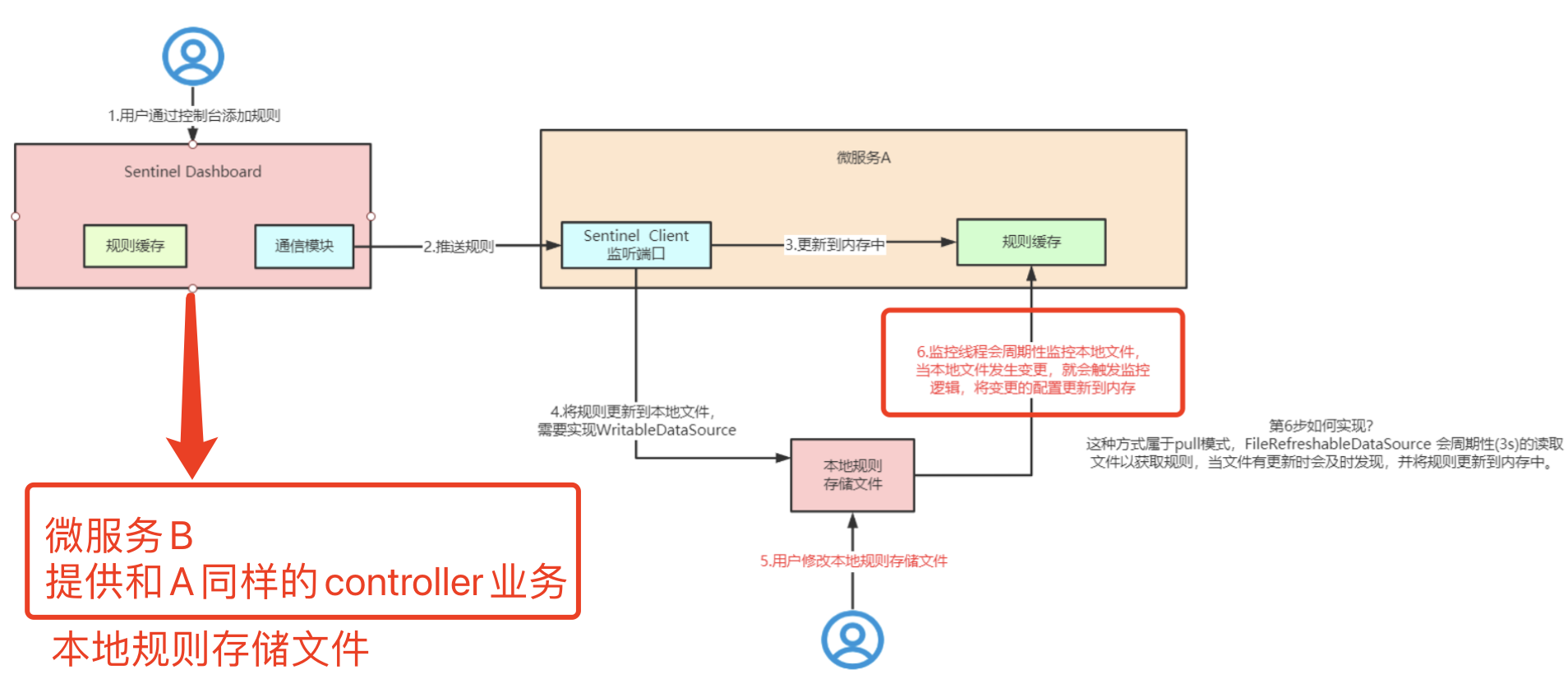
2、多服务推送问题
如果服务B和服务A都提供相同的业务,而用户访问controller时,落到了服务A上,sentinel dashboard 创建某个流控策略时,就会推送给服务A,而服务B 的本地文件则不会有该策略,导致服务B无法达到流控,两台服务之间的流控策略会存在不一致的情况。
3.2 Sentinel Nacos更新内存源码
sentinel client 会去nacos中拉取数据后,更新到内存中。
注意:下面的代码并没有实现更新到内存的代码,而是从nacos中读取配置数据,并且监听nacos的配置文件变化。
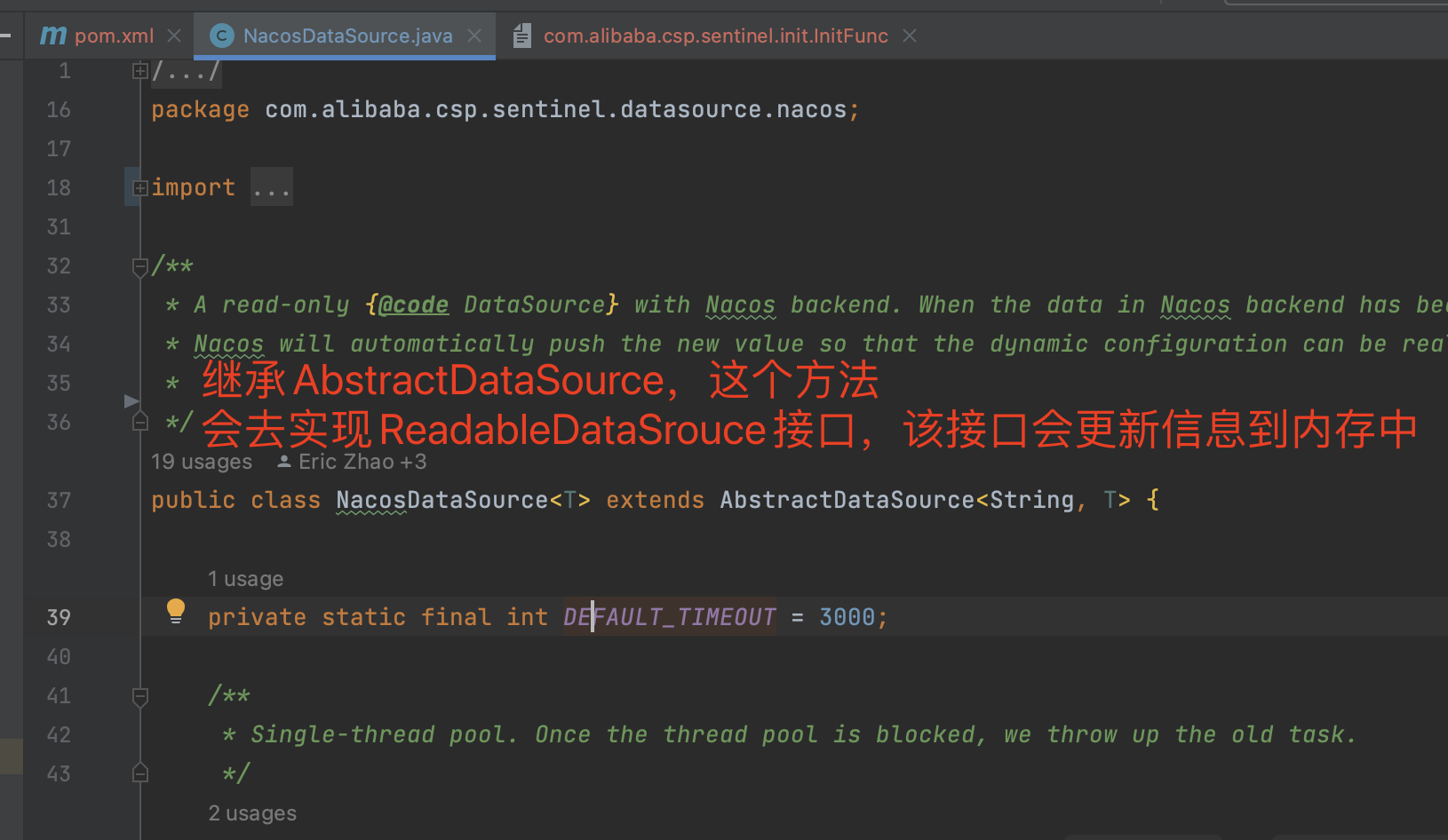
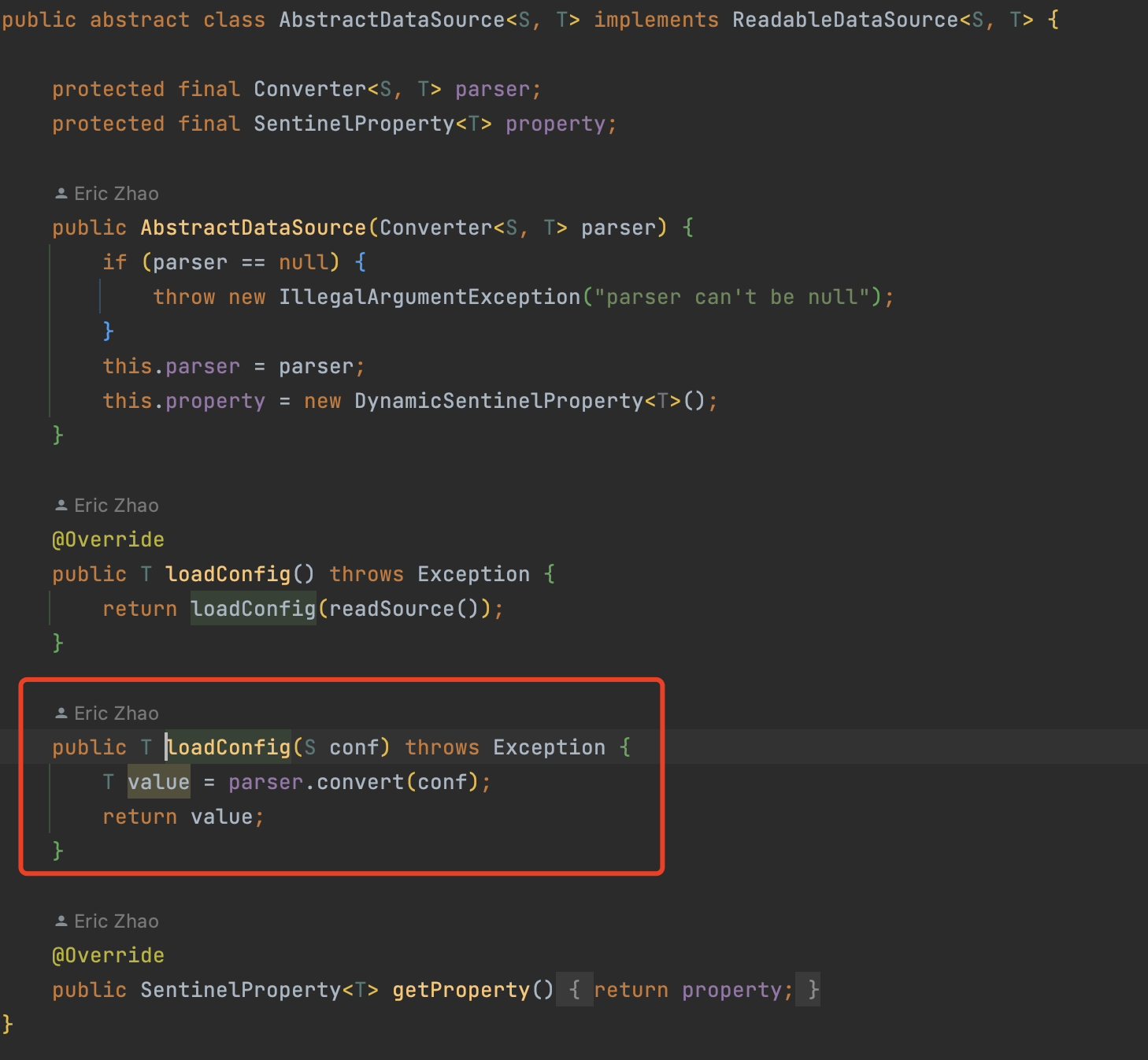
而更新内存的代码,是通过继承AbstractDataSource这个方法,这个方法会去实现ReadableDataSrouce 读数据源接口,AbstractDataSource会把流控策略更新到内存中。
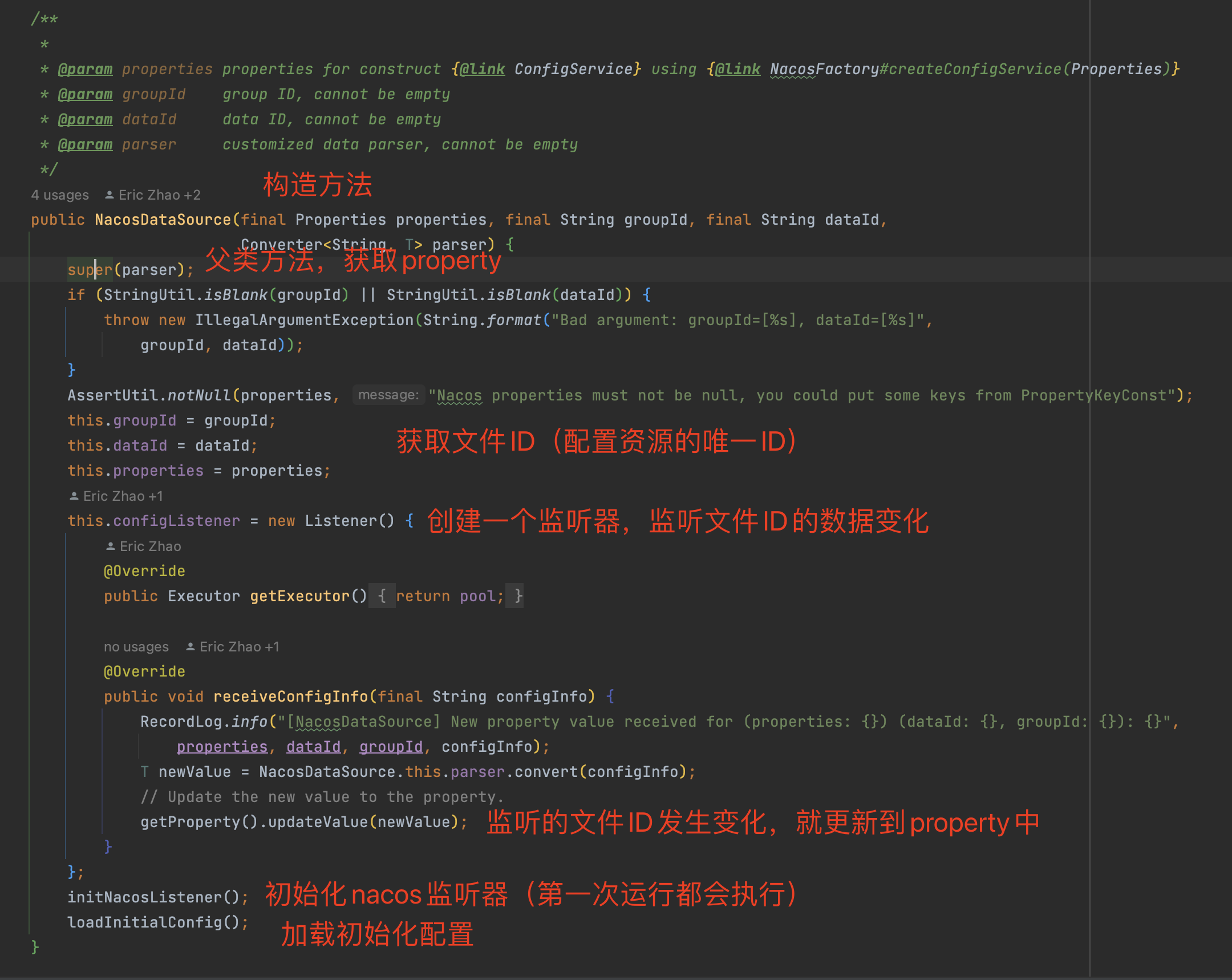
nacos构造方法
构造方法的父类方法会获取到peroperty
从peroperty获取nacos中的数据,并创建一个监听器,监听文件ID的数据变化,如果文件数据发生变化就会更新到内存中
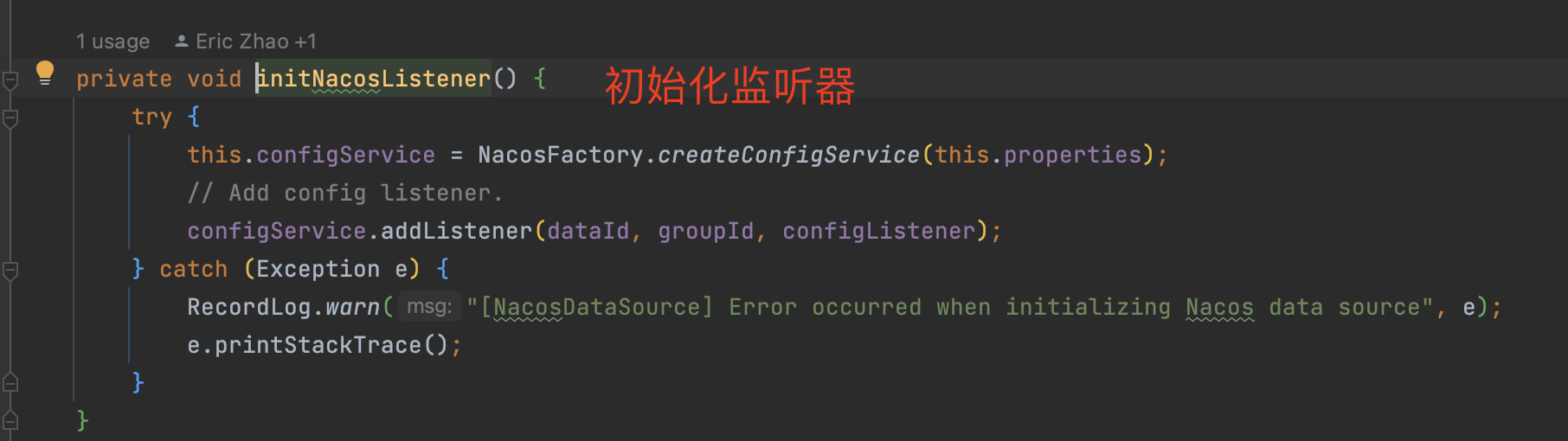
初始化监听器
加载配置数据
完整代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 package com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.nacos;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.concurrent.NamedThreadFactory;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.AbstractDataSource;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.Converter;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.log.RecordLog;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.util.AssertUtil;import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.util.StringUtil;import com.alibaba.nacos.api.NacosFactory;import com.alibaba.nacos.api.PropertyKeyConst;import com.alibaba.nacos.api.config.ConfigService;import com.alibaba.nacos.api.config.listener.Listener;import java.util.Properties;import java.util.concurrent.*;public class NacosDataSource <T> extends AbstractDataSource <String, T> { private static final int DEFAULT_TIMEOUT = 3000 ; private final ExecutorService pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor (1 , 1 , 0 , TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue <Runnable>(1 ), new NamedThreadFactory ("sentinel-nacos-ds-update" , true ), new ThreadPoolExecutor .DiscardOldestPolicy()); private final Listener configListener; private final String groupId; private final String dataId; private final Properties properties; private ConfigService configService = null ; public NacosDataSource (final String serverAddr, final String groupId, final String dataId, Converter<String, T> parser) { this (NacosDataSource.buildProperties(serverAddr), groupId, dataId, parser); } public NacosDataSource (final Properties properties, final String groupId, final String dataId, Converter<String, T> parser) { super (parser); if (StringUtil.isBlank(groupId) || StringUtil.isBlank(dataId)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException (String.format("Bad argument: groupId=[%s], dataId=[%s]" , groupId, dataId)); } AssertUtil.notNull(properties, "Nacos properties must not be null, you could put some keys from PropertyKeyConst" ); this .groupId = groupId; this .dataId = dataId; this .properties = properties; this .configListener = new Listener () { @Override public Executor getExecutor () { return pool; } @Override public void receiveConfigInfo (final String configInfo) { RecordLog.info("[NacosDataSource] New property value received for (properties: {}) (dataId: {}, groupId: {}): {}" , properties, dataId, groupId, configInfo); T newValue = NacosDataSource.this .parser.convert(configInfo); getProperty().updateValue(newValue); } }; initNacosListener(); loadInitialConfig(); } private void loadInitialConfig () { try { T newValue = loadConfig(); if (newValue == null ) { RecordLog.warn("[NacosDataSource] WARN: initial config is null, you may have to check your data source" ); } getProperty().updateValue(newValue); } catch (Exception ex) { RecordLog.warn("[NacosDataSource] Error when loading initial config" , ex); } } private void initNacosListener () { try { this .configService = NacosFactory.createConfigService(this .properties); configService.addListener(dataId, groupId, configListener); } catch (Exception e) { RecordLog.warn("[NacosDataSource] Error occurred when initializing Nacos data source" , e); e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public String readSource () throws Exception { if (configService == null ) { throw new IllegalStateException ("Nacos config service has not been initialized or error occurred" ); } return configService.getConfig(dataId, groupId, DEFAULT_TIMEOUT); } @Override public void close () { if (configService != null ) { configService.removeListener(dataId, groupId, configListener); } pool.shutdownNow(); } private static Properties buildProperties (String serverAddr) { Properties properties = new Properties (); properties.setProperty(PropertyKeyConst.SERVER_ADDR, serverAddr); return properties; } }
实现Push推送模式 生产环境下,一般都使用push推送模式的形式来做持久化,pull模式明显是非常不可取的。
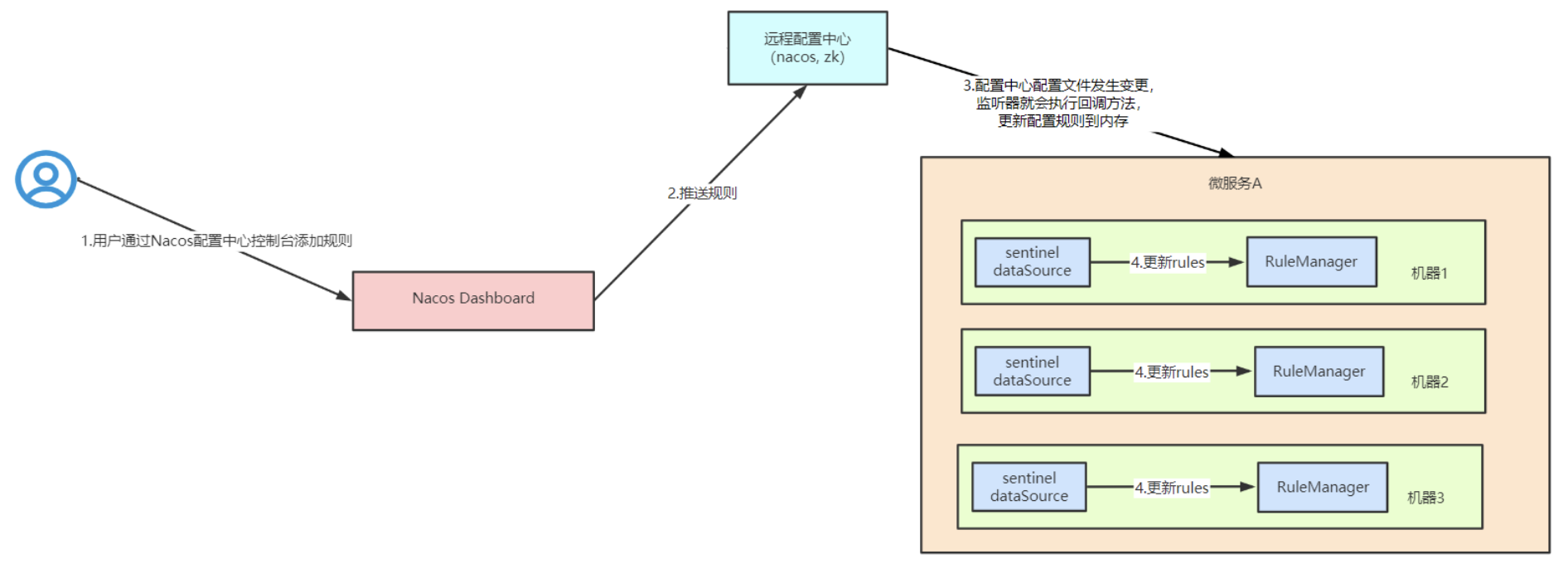
而pull模式和push的区别在于,pull模式是由 微服务客户端主动去本地拉取数据并推送给sentinel dashboard,这明显是不合理的,推送的动作应该由 Nacos(配置中心)或sentinel dashboard来做。
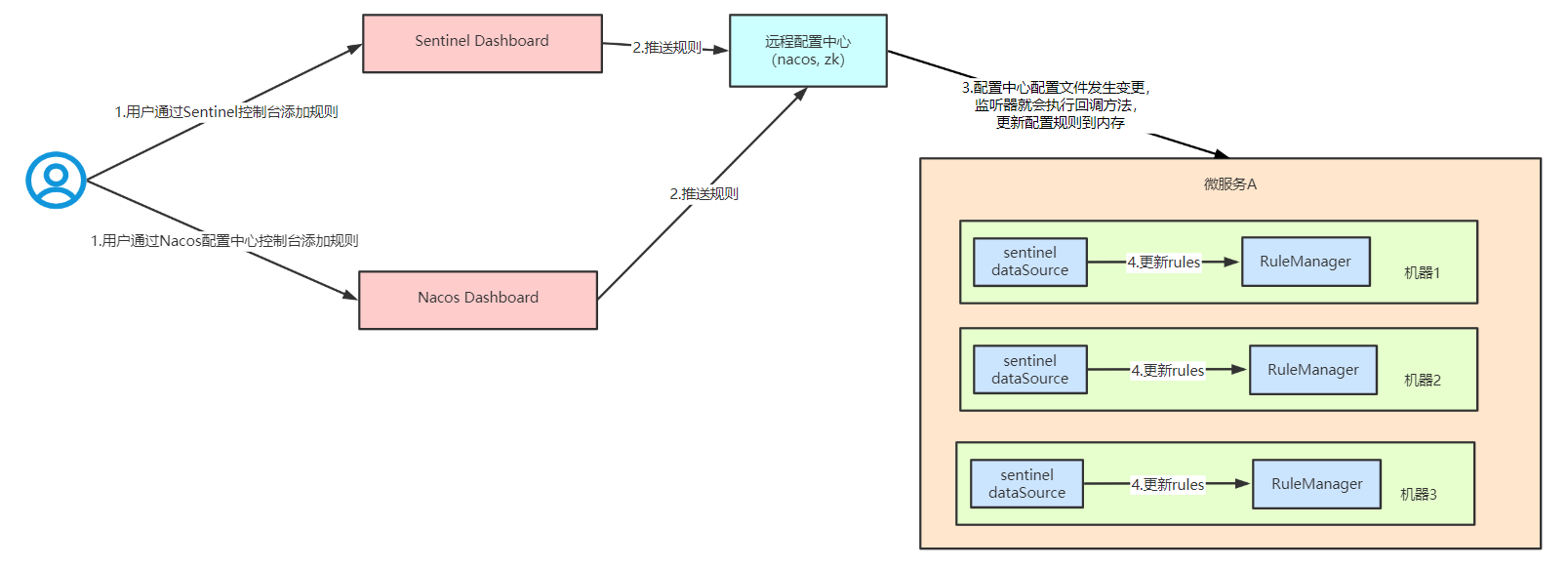
正确做法:sentinel dashboard/nacos控制台推送给配置中心(nacos),nacos推送给 微服务客户端,微服务收到后更新rules到内存。
1)基于Nacos控制台实现推送
用户通过nacos控制台 添加规则
nacos控制台 把规则推送到 nacos(配置中心)
nacos会对该配置进行持久化(看具体的配置,一般建议存入mysql中)
由于微服务启动时,nacos client会监听配置中心的文件ID变化,如果配置文件发生了变化,会触发监听器的回调方法,把配置更新到内存中
源码/工具
springBoot集成sentinel实现nacos push推送模式源码:https://files.javaxing.com/sentinel/SpringSentinelDemo-nacos-push.zip
1.1 引入依赖 1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > com.alibaba.csp</groupId > <artifactId > sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId > </dependency >
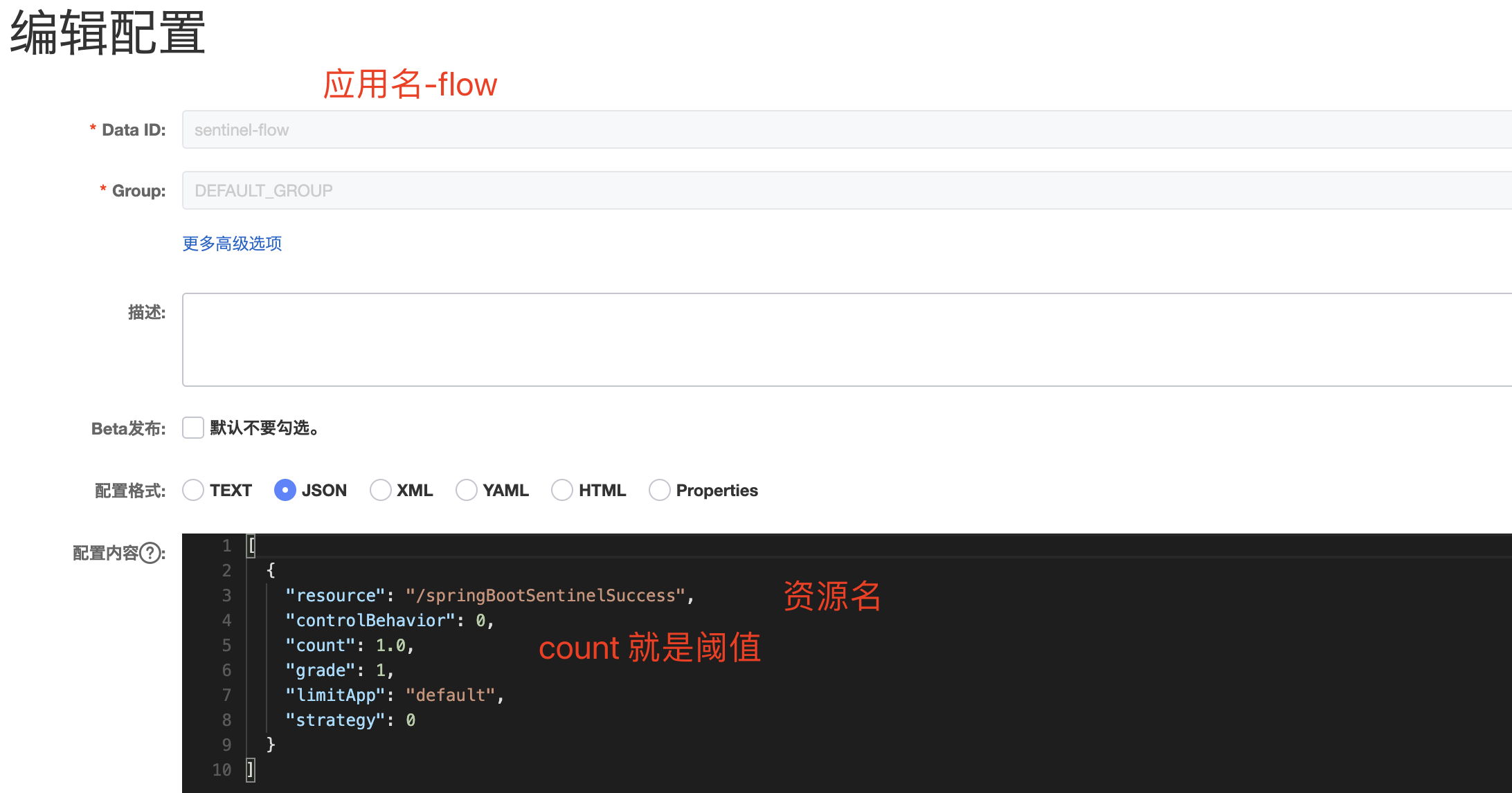
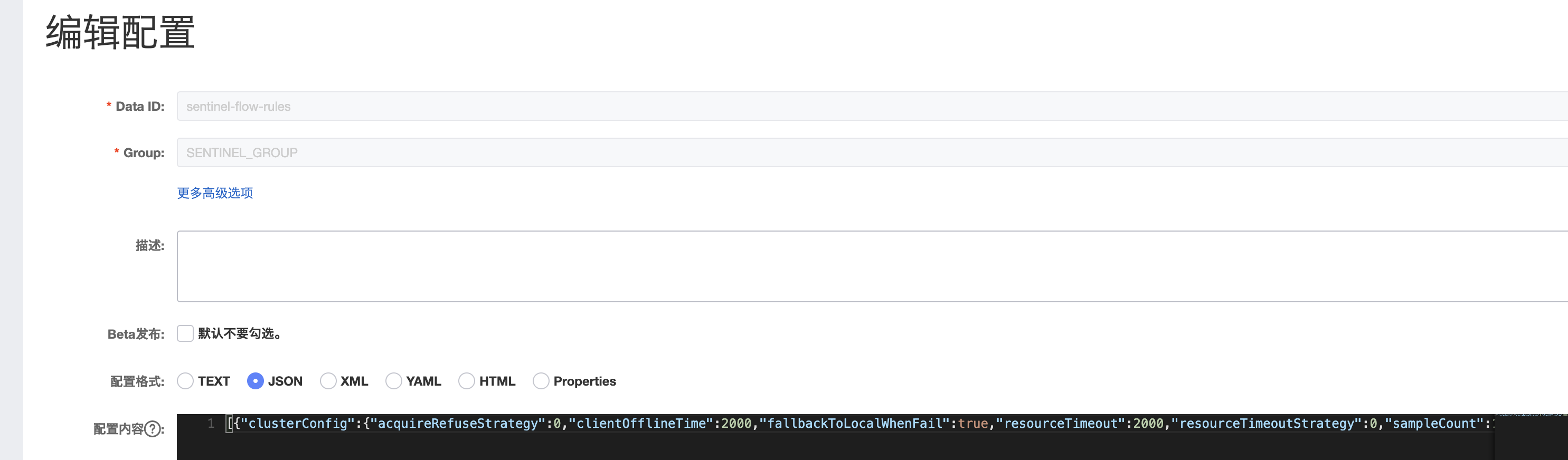
1.2 nacos配置中心配置策略 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 [ { "resource" : "/springBootSentinelSuccess" , "controlBehavior" : 0 , "count" : 1.0 , "grade" : 1 , "limitApp" : "default" , "strategy" : 0 } ]
1.3 配置yml 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 spring: application: name: sentinel cloud: nacos: config: server-addr: 10.211 .55 .12 :8848 discovery: server-addr: 10.211 .55 .12 :8848 sentinel: transport: dashboard: 10.211 .55 .12 :9991 web-context-unify: false datasource: ds1: nacos: server-addr: 10.211 .55 .12 :8848 dataId: ${spring.application.name}-flow groupId: DEFAULT_GROUP data-type: json rule-type: flow management: endpoints: web: exposure: include: '*'
1.4 sentinel dashboard
nacos配置策略后,会推送给微服务。微服务收到策略后会更新到内存中,而sentinel dashboard 会从微服务内存中获取数据。
1.5 该方法缺点 直接在Sentinel Dashboard中修改规则配置
因为我们sentinel dashboard的数据来自微服务内存,sentinel dash修改策略后,也只会推送给微服务内存,并不会推送给nacos。
为了解决这个问题,我们得采用第二种办法,修改sentinel dashboard源码,让dashboard修改策略后推送给nacos。
2)基于Sentinel控制台实现推送(推荐) 除了nacos外,我们也可以通过sentinel dashboard来实现推送,思路为:
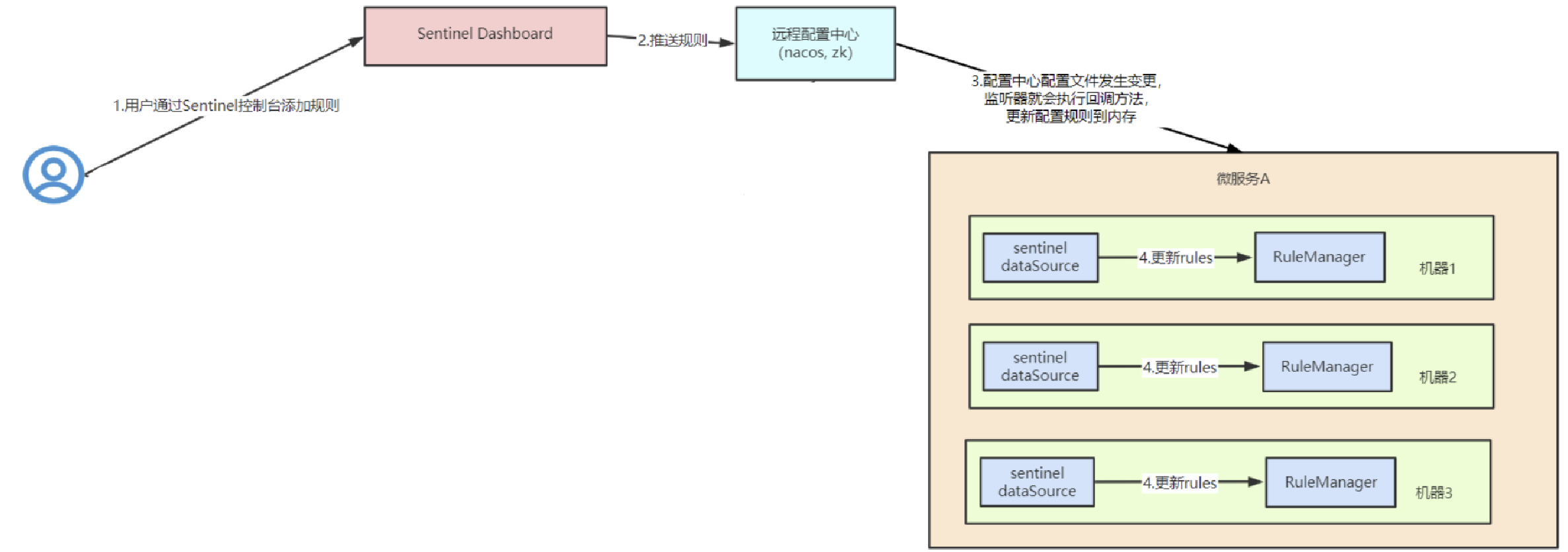
用户通过sentinel dashboard 添加规则
sentinel dashboard把规则推送到 nacos(配置中心)
nacos会对该配置进行持久化(看具体的配置,一般建议存入mysql中)
由于微服务启动时,nacos client会监听配置中心的文件ID变化,如果配置文件发生了变化,会触发监听器的回调方法,把配置更新到内存中
从 Sentinel 1.4.0 开始,Sentinel 控制台提供 DynamicRulePublisher 和 DynamicRuleProvider 接口用于实现应用维度的规则推送和拉取:
DynamicRuleProvider: 拉取规则
DynamicRulePublisher: 推送规则
源码/工具
springBoot集成sentinel实现dashboard push推送模式源码:https://files.javaxing.com/sentinel/SpringSentinelDemo.zip
sentinel dashboard改造后的jar包:https://files.javaxing.com/sentinel/sentinel-dashboard-push.jar
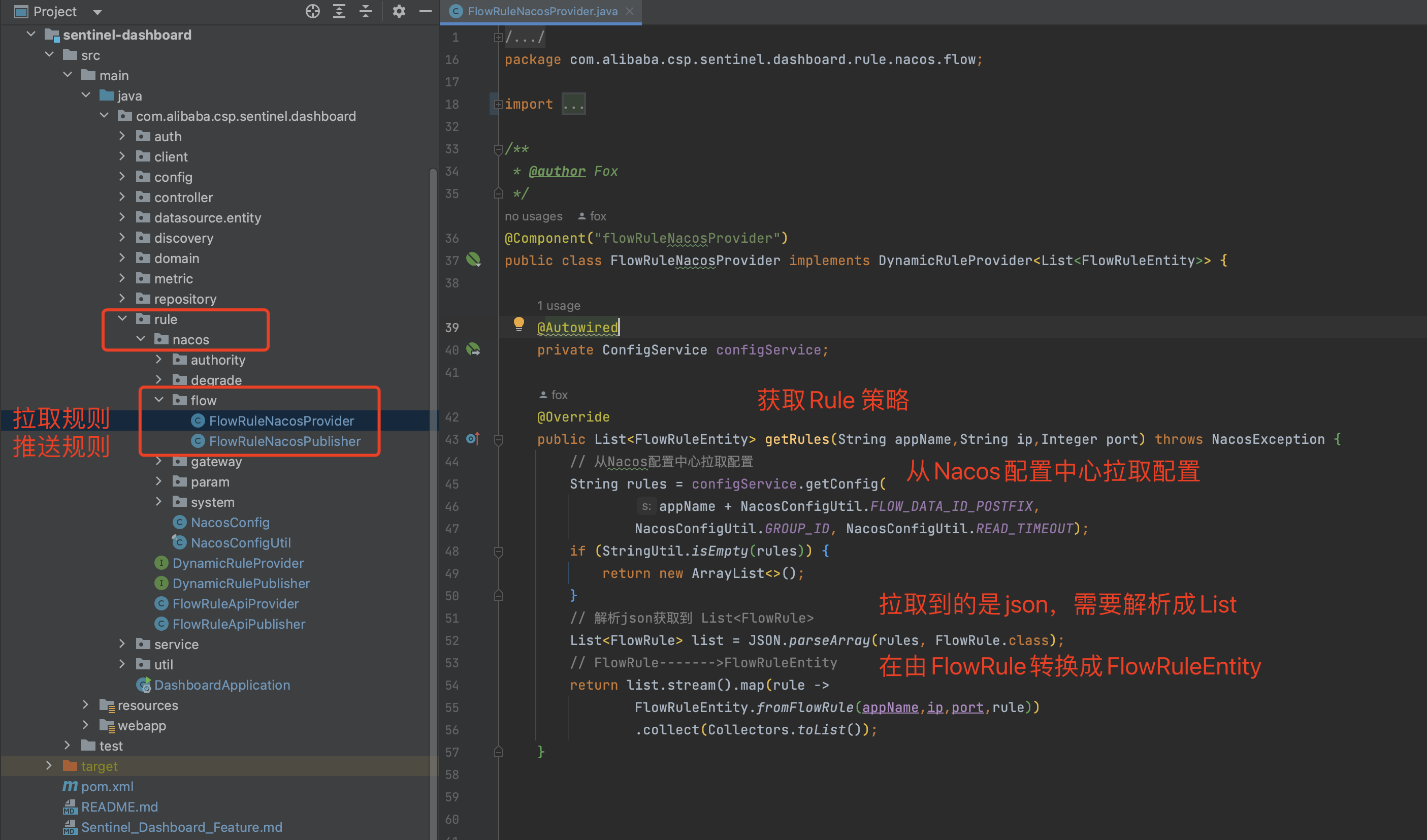
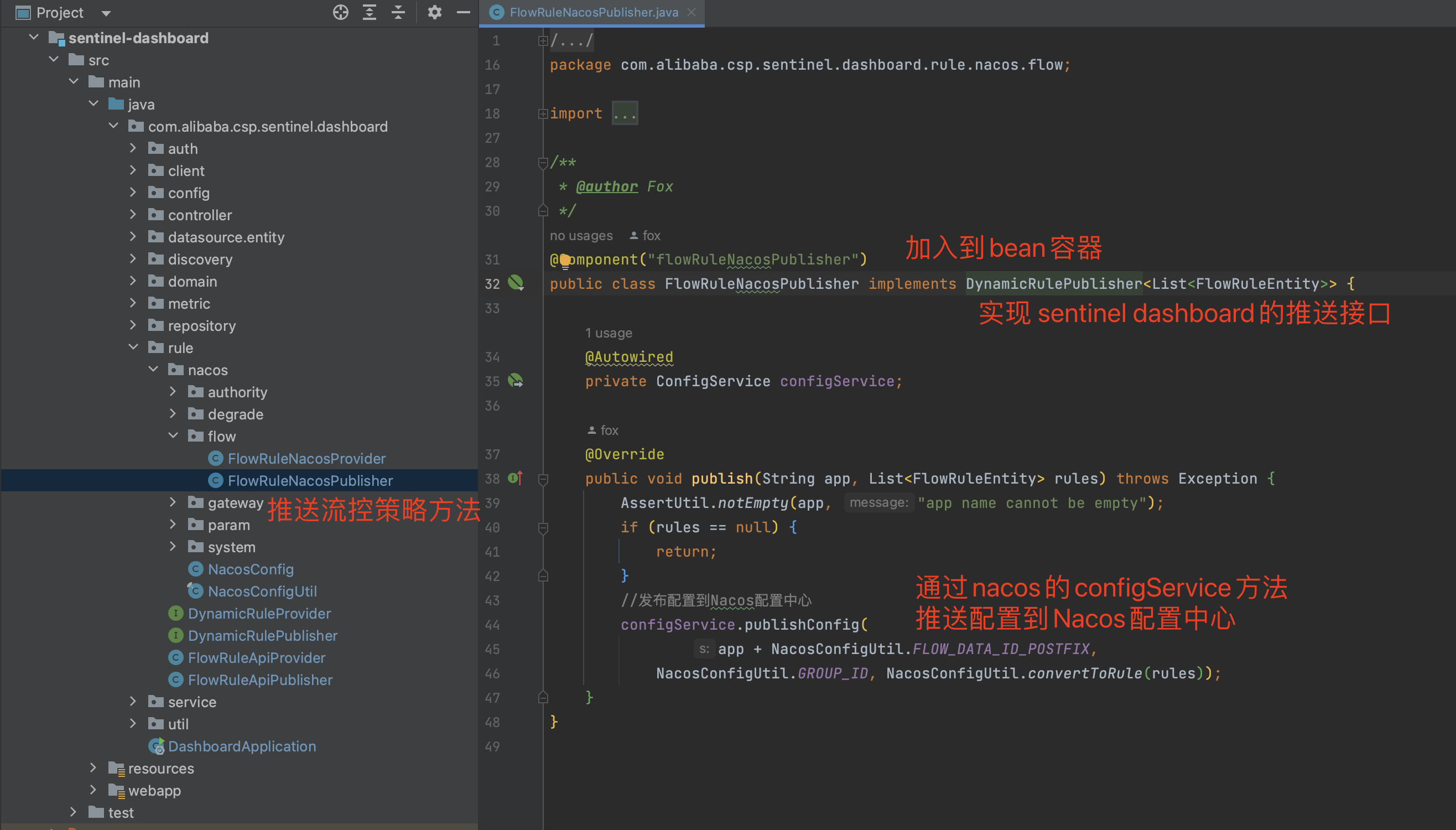
2.1 规则拉取和规则推送实现方法 在com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.dashboard.rule包下创建nacos包,然后把各种场景的配置规则拉取和推送的实现类写到此包下:
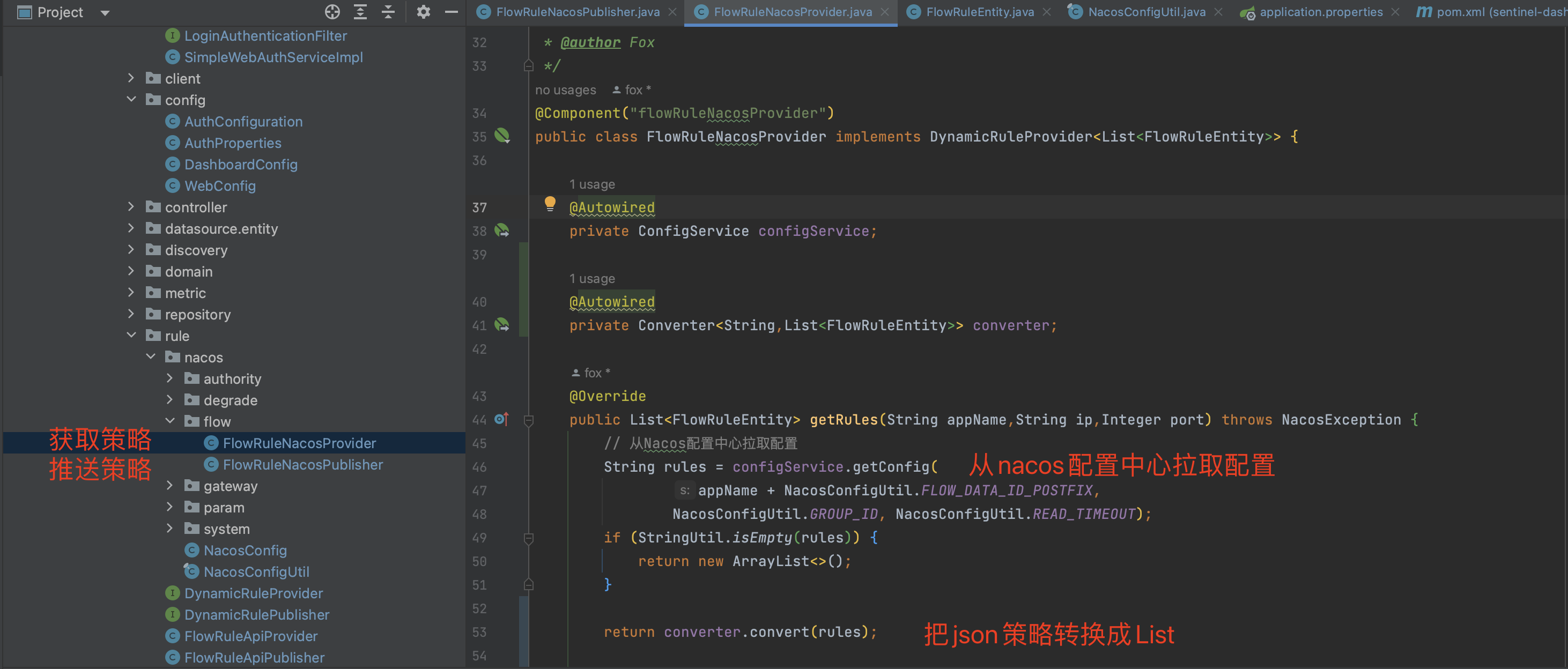
从Nacos拉取规则
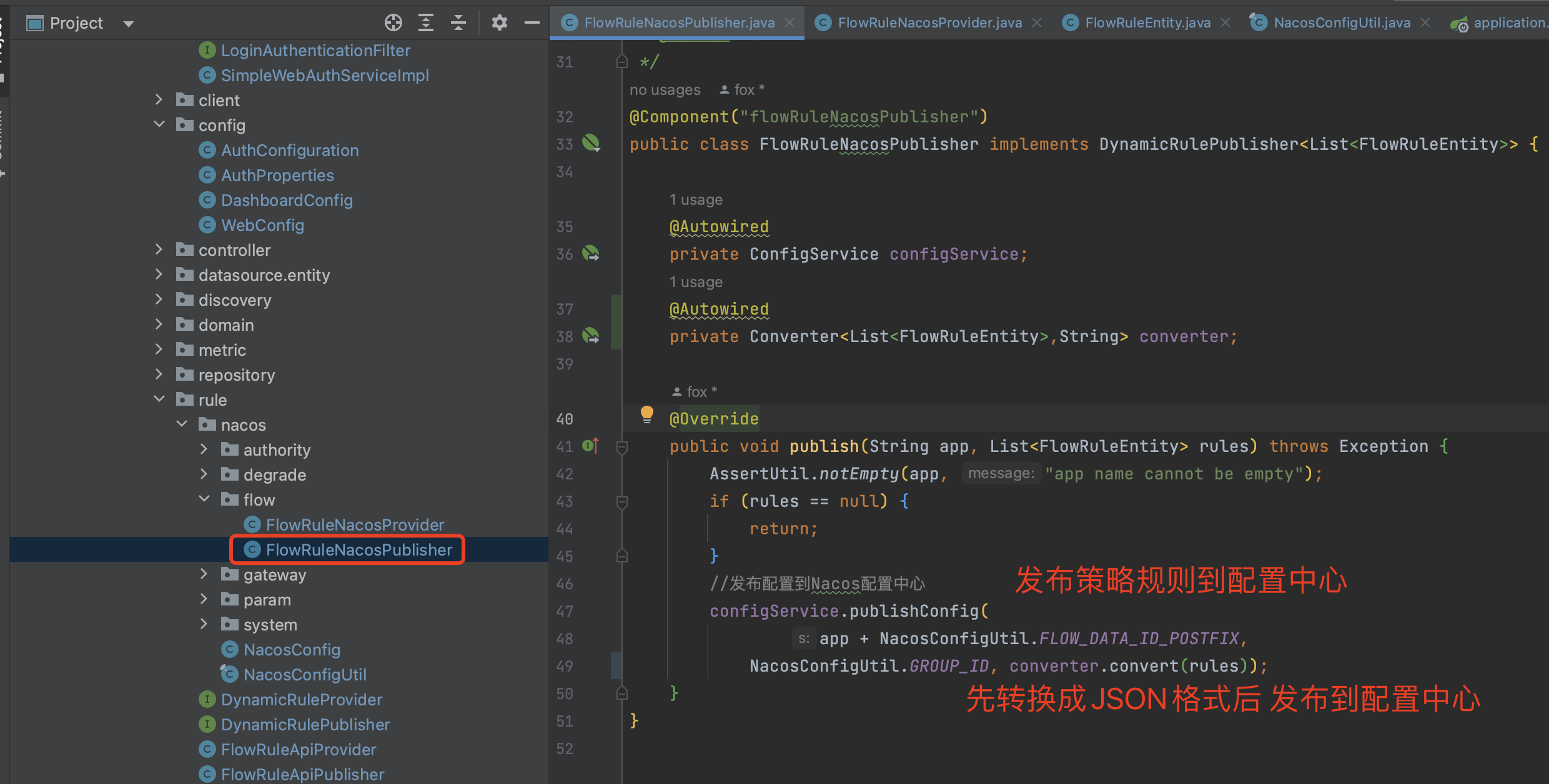
推送规则到Nacos
2.2 控制台从nacos拉取策略
我们修改控制台获取策略的controller,让其从nacos中拉取策略。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 @Autowired @Qualifier("flowRuleNacosProvider") private DynamicRuleProvider<List<FlowRuleEntity>> ruleProvider; @Autowired @Qualifier("flowRuleNacosPublisher") private DynamicRulePublisher<List<FlowRuleEntity>> rulePublisher; @GetMapping("/rules") @AuthAction(PrivilegeType.READ_RULE) public Result<List<FlowRuleEntity>> apiQueryMachineRules (@RequestParam String app, @RequestParam String ip, @RequestParam Integer port) { if (StringUtil.isEmpty(app)) { return Result.ofFail(-1 , "app can't be null or empty" ); } if (StringUtil.isEmpty(ip)) { return Result.ofFail(-1 , "ip can't be null or empty" ); } if (port == null ) { return Result.ofFail(-1 , "port can't be null" ); } try { List<FlowRuleEntity> rules = ruleProvider.getRules(app,ip,port); if (rules != null && !rules.isEmpty()) { for (FlowRuleEntity entity : rules) { entity.setApp(app); if (entity.getClusterConfig() != null && entity.getClusterConfig().getFlowId() != null ) { entity.setId(entity.getClusterConfig().getFlowId()); } } } rules = repository.saveAll(rules); return Result.ofSuccess(rules); } catch (Throwable throwable) { logger.error("Error when querying flow rules" , throwable); return Result.ofThrowable(-1 , throwable); } }
2.3 控制台推送策略到nacos
我们修改控制台新增策略的controller,让其收到策略后推送到nacos 配置中心。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 @PostMapping("/rule") @AuthAction(PrivilegeType.WRITE_RULE) public Result<FlowRuleEntity> apiAddFlowRule (@RequestBody FlowRuleEntity entity) { Result<FlowRuleEntity> checkResult = checkEntityInternal(entity); if (checkResult != null ) { return checkResult; } entity.setId(null ); Date date = new Date (); entity.setGmtCreate(date); entity.setGmtModified(date); entity.setLimitApp(entity.getLimitApp().trim()); entity.setResource(entity.getResource().trim()); try { entity = repository.save(entity); publishRules(entity.getApp()); return Result.ofSuccess(entity); } catch (Throwable t) { Throwable e = t instanceof ExecutionException ? t.getCause() : t; logger.error("Failed to add new flow rule, app={}, ip={}" , entity.getApp(), entity.getIp(), e); return Result.ofFail(-1 , e.getMessage()); } } private <R> Result<R> checkEntityInternal (FlowRuleEntity entity) { if (StringUtil.isBlank(entity.getApp())) { return Result.ofFail(-1 , "app can't be null or empty" ); } if (StringUtil.isBlank(entity.getIp())) { return Result.ofFail(-1 , "ip can't be null or empty" ); } if (entity.getPort() == null ) { return Result.ofFail(-1 , "port can't be null" ); } if (StringUtil.isBlank(entity.getLimitApp())) { return Result.ofFail(-1 , "limitApp can't be null or empty" ); } if (StringUtil.isBlank(entity.getResource())) { return Result.ofFail(-1 , "resource can't be null or empty" ); } if (entity.getGrade() == null ) { return Result.ofFail(-1 , "grade can't be null" ); } if (entity.getGrade() != 0 && entity.getGrade() != 1 ) { return Result.ofFail(-1 , "grade must be 0 or 1, but " + entity.getGrade() + " got" ); } if (entity.getCount() == null || entity.getCount() < 0 ) { return Result.ofFail(-1 , "count should be at lease zero" ); } if (entity.getStrategy() == null ) { return Result.ofFail(-1 , "strategy can't be null" ); } if (entity.getStrategy() != 0 && StringUtil.isBlank(entity.getRefResource())) { return Result.ofFail(-1 , "refResource can't be null or empty when strategy!=0" ); } if (entity.getControlBehavior() == null ) { return Result.ofFail(-1 , "controlBehavior can't be null" ); } int controlBehavior = entity.getControlBehavior(); if (controlBehavior == 1 && entity.getWarmUpPeriodSec() == null ) { return Result.ofFail(-1 , "warmUpPeriodSec can't be null when controlBehavior==1" ); } if (controlBehavior == 2 && entity.getMaxQueueingTimeMs() == null ) { return Result.ofFail(-1 , "maxQueueingTimeMs can't be null when controlBehavior==2" ); } if (entity.isClusterMode() && entity.getClusterConfig() == null ) { return Result.ofFail(-1 , "cluster config should be valid" ); } return null ; } private void publishRules ( String app) throws Exception { List<FlowRuleEntity> rules = repository.findAllByApp(app); rulePublisher.publish(app, rules); }
2.4 微服务接入新的sentinel dashboard 引入依赖
引入sentinel nacos数据源的依赖
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > com.alibaba.csp</groupId > <artifactId > sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId > </dependency >
修改yml配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 spring: application: name: sentinel cloud: nacos: config: server-addr: 10.211 .55 .12 :8848 discovery: server-addr: 10.211 .55 .12 :8848 sentinel: transport: dashboard: 10.211 .55 .12 :9991 web-context-unify: false datasource: flow-rules: nacos: server-addr: 10.211 .55 .12 :8848 dataId: ${spring.application.name}-flow-rules groupId: SENTINEL_GROUP data-type: json rule-type: flow degrade-rules: nacos: server-addr: 10.211 .55 .12 :8848 dataId: ${spring.application.name}-degrade-rules groupId: SENTINEL_GROUP data-type: json rule-type: degrade param-flow-rules: nacos: server-addr: 10.211 .55 .12 :8848 dataId: ${spring.application.name}-param-flow-rules groupId: SENTINEL_GROUP data-type: json rule-type: param-flow authority-rules: nacos: server-addr: 10.211 .55 .12 :8848 dataId: ${spring.application.name}-authority-rules groupId: SENTINEL_GROUP data-type: json rule-type: authority system-rules: nacos: server-addr: 10.211 .55 .12 :8848 dataId: ${spring.application.name}-system-rules groupId: SENTINEL_GROUP data-type: json rule-type: system management: endpoints: web: exposure: include: '*'
需要指定流控策略,热点参数,熔断策略等 数据源的策略来源,sentinel.transport.datasource.flow-rules
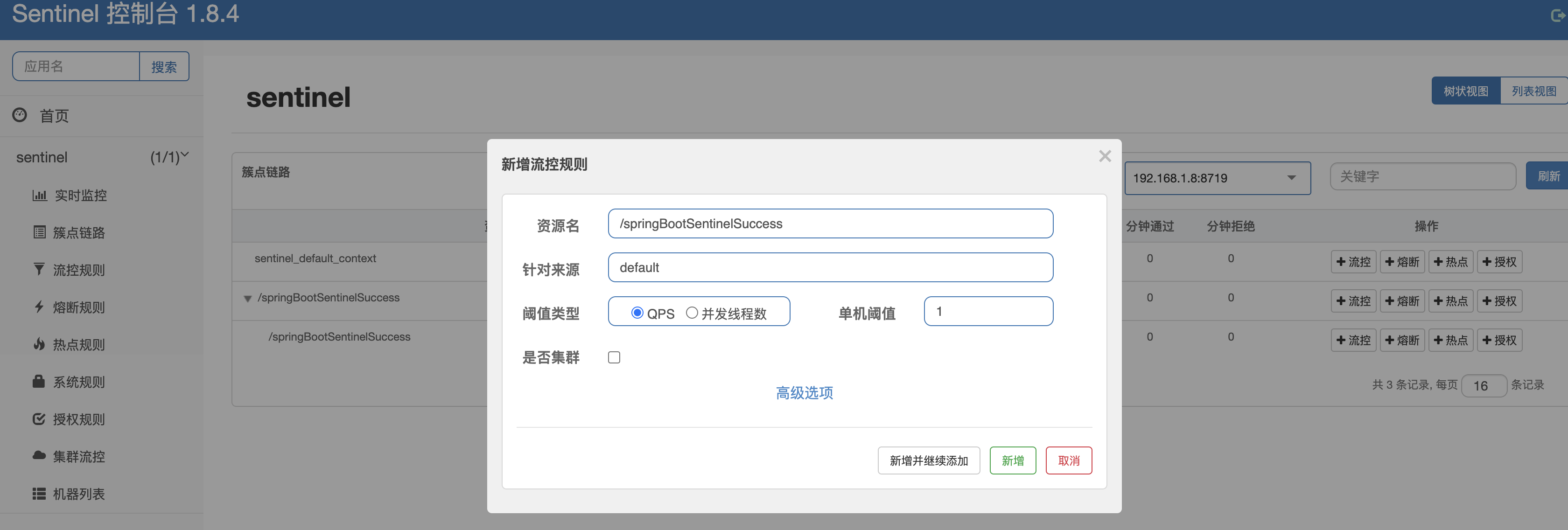
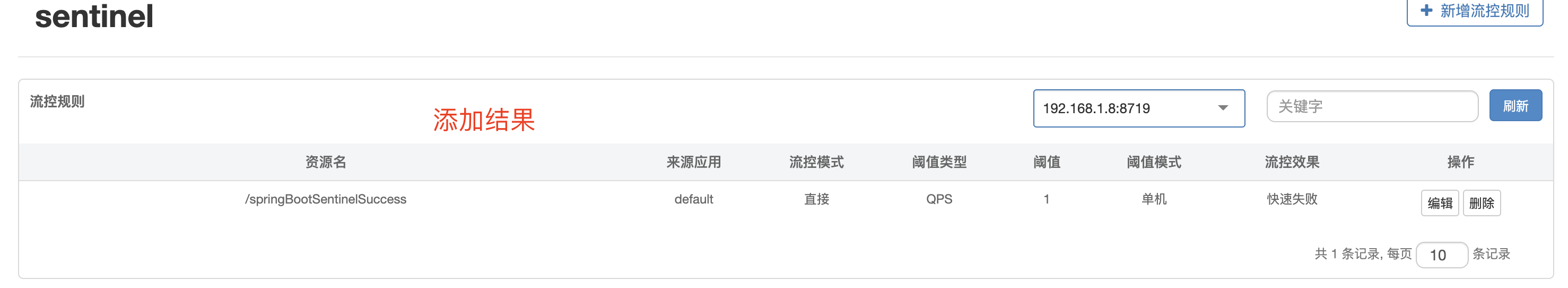
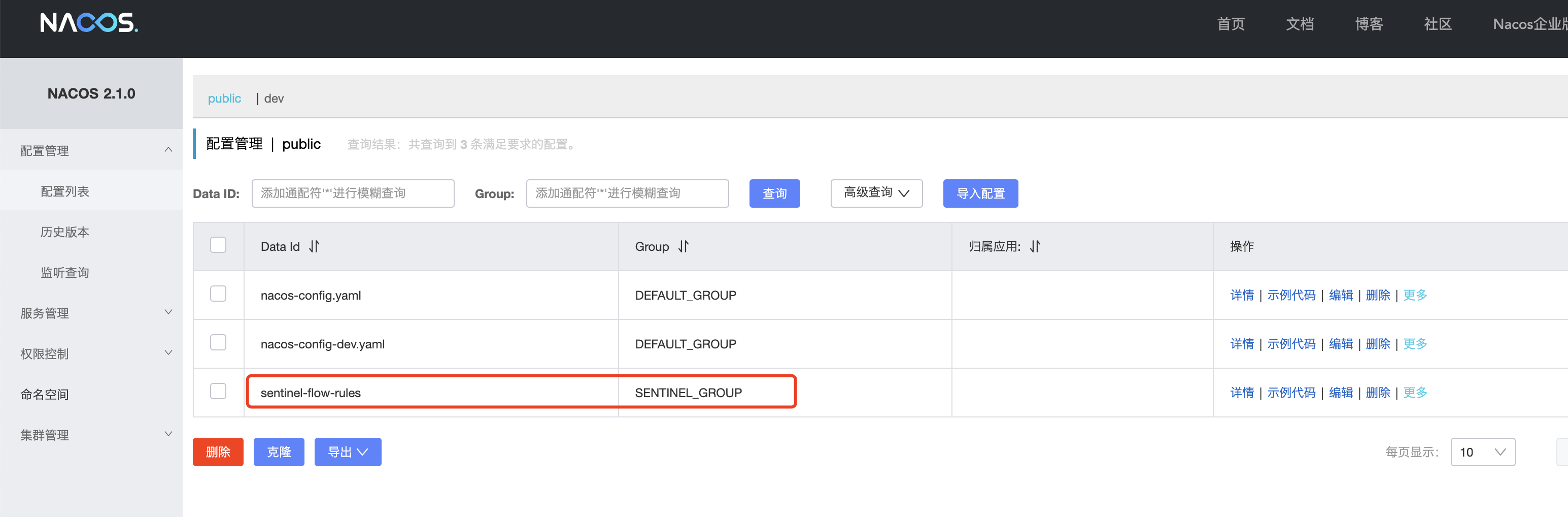
sentinel dashboard添加流控策略
Nacos查看配置文件
当我们在sentinel dashboard配置流控策略后,会推送到nacos,所以我们在nacos中是可以看到对应的策略的。
测试接口
2.5 热点参数策略失效问题 注意:控制台改造后有可能出现规则不生效的情况,比如热点参数规则因为Converter解析json错误的原因会导致不生效。
参见源码:com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.AbstractDataSource#loadConfig(S) 会解析配置规则。
原因是:改造dashboard,提交到nacos配置中心的数据是ParamFlowRuleEntity类型,微服务拉取配置要解析的是ParamFlowRule类型,会导致规则解析丢失数据,造成热点规则不生效。 其他的规则原理也是一样,存在失效的风险。
2.6 解决热点参数策略失效 解决方案一 自定义解析器 自定义一个解析热点规则配置的解析器FlowParamJsonConverter,继承JsonConverter,重写convert方法。然后利用后置处理器替换beanName为”param-flow-rules-sentinel-nacos-datasource”的converter属性,注入FlowParamJsonConverter。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 @Configuration public class ConverterConfig { @Bean("sentinel-json-param-flow-converter2") @Primary public JsonConverter jsonParamFlowConverter () { return new FlowParamJsonConverter (new ObjectMapper (), ParamFlowRule.class); } } @Component public class FlowParamConverterBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { @Autowired private JsonConverter jsonParamFlowConverter; @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (beanName.equals("param-flow-rules-sentinel-nacos-datasource" )) { NacosDataSourceFactoryBean nacosDataSourceFactoryBean = (NacosDataSourceFactoryBean) bean; nacosDataSourceFactoryBean.setConverter(jsonParamFlowConverter); return bean; } return bean; } } public class FlowParamJsonConverter extends JsonConverter { Class ruleClass; public FlowParamJsonConverter (ObjectMapper objectMapper, Class ruleClass) { super (objectMapper, ruleClass); this .ruleClass = ruleClass; } @Override public Collection<Object> convert (String source) { List<Object> list = new ArrayList <>(); JSONArray jsonArray = JSON.parseArray(source); for (int i = 0 ; i < jsonArray.size(); i++) { JSONObject jsonObject = (JSONObject) jsonArray.getJSONObject(i).get("rule" ); Object object = JSON.toJavaObject(jsonObject, ruleClass); list.add(object); } return list; } }
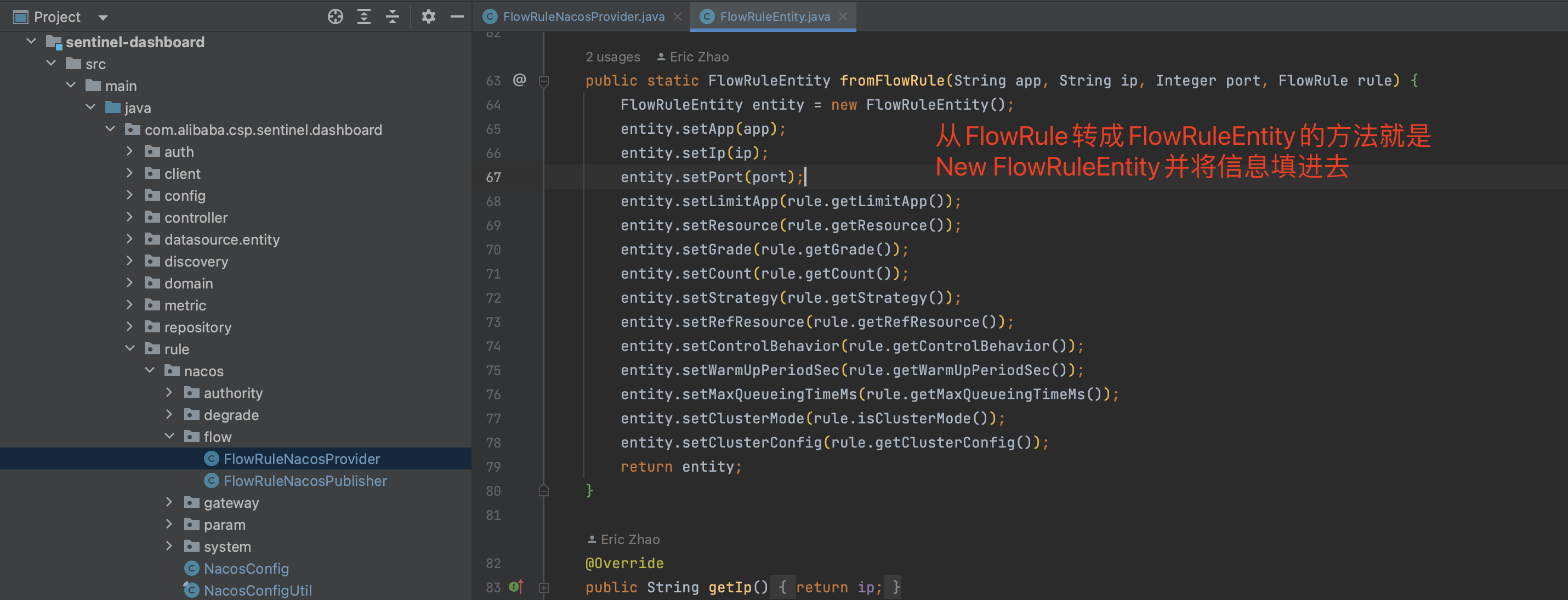
解决方案二 实体类转换(推荐) 改造Sentinel Dashboard控制台,发布配置时将ParamFlowRuleEntity转成ParamFlowRule类型 从配置中心拉取配置后将ParamFlowRule转成ParamFlowRuleEntity。
从nacos拉取规则策略
从配置中心拉取配置到控制台时,FlowRule转换为FlowRuleEntity
推送规则到Nacos
将参数的类型从 FlowRuleEntity转成FlowRule类型(RuleEntity)